NPG Reliability
and Development
»
Operational
Activities
Electricity transmission
Transmission of electricity in KEGOC grids
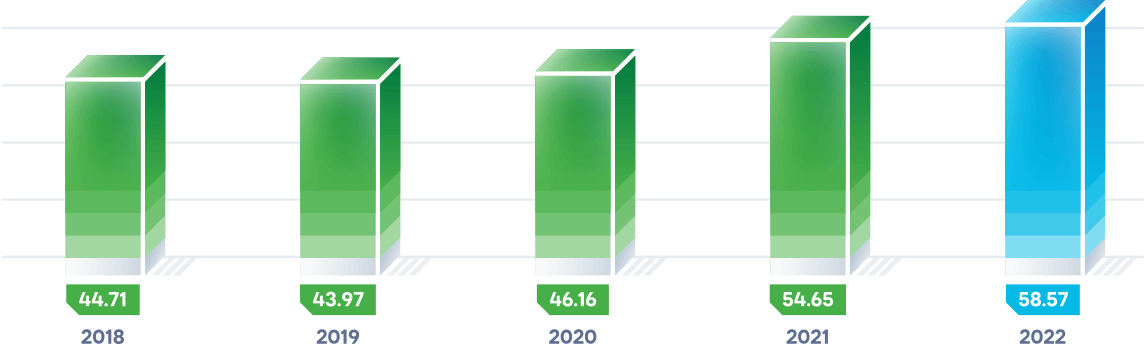
In 2022, the actual volume of energy transmission services in the national power grid was 58.57 billion kWh, up 3.9 billion kWh or 7.2% over 2021. The main reasons for the excess are:
- an increase in the volume of electricity transmission for the Republic of Kazakhstan’s wholesale market entities of 2.446 billion kWh, or 5%, compared to 2021; and
- an increase of 2.096 billion kWh, or 53%, in inter-state electricity transit (Russia - Kazakhstan - Russia).
According to the terms of the contract between KEGOC and RosSeti, electricity transmission (transit) was performed by KEGOC grids along the Russia-Kazakhstan-Russia route in 2022. This transit system provided a total of 6,053.5 million kWh in services.
Technical
dispatching
Technical
dispatching
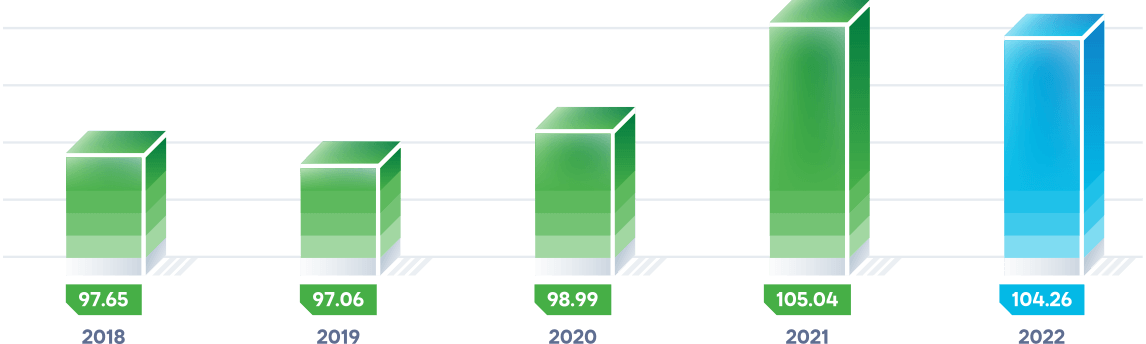
The actual volume of rendered services on technical dispatching of electricity generation and consumption in the grid in 2022 was 104.26 billion kWh, which was 779 million kWh or 0.7% lower than in 2021 due to a decrease in power generation by Kazakhstan’s power generating organisations.
Electricity
generation-consumption
balancing
Electricity
generation-consumption
balancing
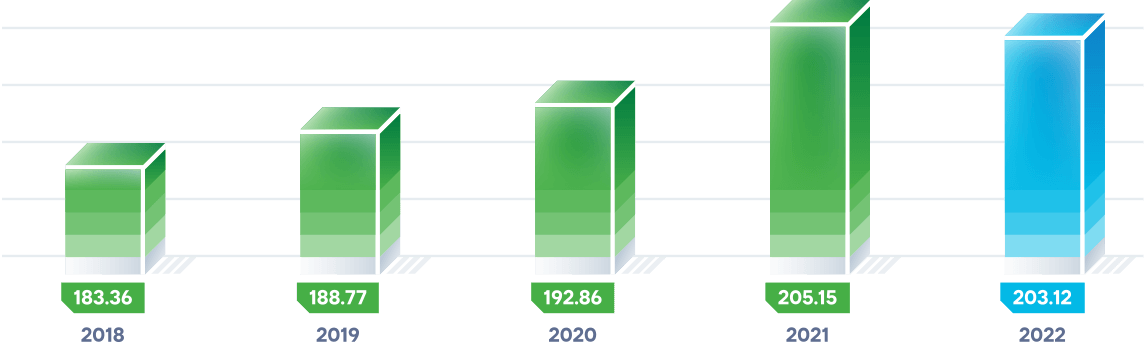
The actual amount of electricity generation-consumption balancing services in 2022 was 203.12 billion kWh, which was 2.03 billion kWh, or 1%, less than in 2021 due to a decline in power generation-consumption in Kazakhstan’s wholesale market.
Electricity
purchase and
sale transactions
In line with the Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan ‘On Electric Power Industry’, KEGOC serves as the system operator of the Republic of Kazakhstan’s UPS for interaction with surrounding states’ power systems in order to manage and ensure the stability of the parallel operation.
In 2022, KEGOC paid KZT 28,394.5 million (20.05 KZT / kWh) for 1,416.2 million kWh of electricity to compensate for hourly unscheduled deviations of the actual interstate power flow balance at the border of Kazakhstan UPS of and Russia UES.
KEGOC sold 1,416.2 million kWh for KZT 10,457.9 million (7.38 KZT/kWh) to compensate for hourly unscheduled deviations of the actual interstate power flow balance at the border of Kazakhstan UPS of and Russia UES.
Investment
Activities
Rapid development of the electricity sector, including the power grid infrastructure, is required to ensure steady growth of the nation’s economy.
The Company actively keeps putting large-scale investment projects into operation in order to increase efficiency, strengthen the reliability of NPG operation, and grid capacity. These initiatives are carried out with consideration for the development of renewable energy (PVPPs and WPPs, which are notorious for their intermitted generation), as well as for the suitable design of the power grid to guarantee the capacity output of major RES facilities.
The Company carried out the following significant investment projects and activities in 2022:
Rehabilitation of 220-500 kV OHTL
at Aktyubinskiye MES branch, Sarbaiskiye MES branch and Zapadnye MES branch of KEGOC, phase 1.
Project objective
Large-scale project to upgrade and rehabilitate 24 overhead lines.
Source of funding
Financing for the project comes from equity funds and borrowed funds raised through the listing of KEGOC green bonds on the trading floor of the Kazakhstan Stock Exchange (KASE).
Status of project implementation
- Construction and installation work was finished on 20 of 24 transmission lines in 2022, and these activities were completed on 18 transmission lines, 16 of which were commissioned.
- Since the project’s inception, 1,749 km of the 2,029 km of overhead lines have been restored, including 442.3 km in 2022.
Capital expenditure
in 2022 amounted to
11.1
West Kazakhstan Electricity Transmission Reinforcement Project.
Project objective
Increase the transmission capacity and reliability of power supply to consumers in Zone West of the UPS of Kazakhstan by reinforcing 220 kV power grids connecting western regions of Kazakhstan.
Source of funding
Financing for the project comes from equity funds and borrowed funds raised through the listing of KEGOC green bonds on the trading floor of the Kazakhstan Stock Exchange (KASE).
Status of project implementation
In 2022, construction and installation work was in progress:
- since the start of the project 2,898 (69%) out of 4,182 towers have been installed, including 1,760 (42%) in 2022;
- since the start of the project, 297.8 km of 779.7 km (38%) of conductor have been installed, including 244.4 km in 2022;
- construction and installation work was carried out on 220 kV Uralskaya, Pravoberezhnaya, Inder, Kulsary, Tengiz and 220 kV Karabatan substations.
Capital investments
in 2022 amounted to
19.2
Turkestan External Power Supply Reinforcement Project.
Project objective
Providing conditions for the development of the local electricity distribution network of 110 kV and below in accordance with the Comprehensive Plan for socio-economic development of Turkestan Oblast until 2024, and the Road Map for the implementation of priority measures for the development of Turkestan.
Source of funding
Company’s equity funds.
Status of project implementation
- The Company finished construction, installation, and commissioning work in 2022. A new 220 kV Ortalyk substation near Turkestan has been built, which will be used as a connection point of the local 110 kV and lower electricity distribution network.
-
The facility was put into operation on 28 October 2022.
The capital expenditure
in 2022 was
2.0
KEGOC builds its investment project portfolio using a scenario methodology based on the evolution and annual update of Kazakhstan’s expected balance of energy and generation capacity. Furthermore, climate change risks, particularly natural factors (floods, hurricanes, earthquakes, epidemics) that contribute to the formation of emergency hazards, are considered. In order to assure grid reliability and reduce the key risk of operational asset failure, the Company intends to implement the following NPG development investment projects in the near future:
- South Kazakhstan Electricity Transmission Reinforcement Project.
- The project envisages the reinforcement of the power system of Zone South of the UPS of Kazakhstan across the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan to ensure the reliability of power supply to consumers in Zone South and to strengthen the power connection between the regions of Zone South.
- Based on the results of the feasibility study, the construction of two 500 kV Shu-Zhambyl and Zhambyl-Shymkent overhead lines was approved, as well as the reinforcement of 220 kV networks of the Almaty power region.
- The project shall be completed in 2027.
- West Kazakhstan Power System Interconnection Project.
- The project envisages the interconnection of Zone West of Kazakhstan with the main part of the UPS to ensure energy security and energy independence of the western regions of Kazakhstan and to improve the reliability of electricity supply to consumers in Zone West.
- A feasibility study for the project is currently underway. It shall determine the main option for the construction of the transmission line based on the plans to develop generating capacity and prospective investment projects of consumers.
- The approximate deadline for project implementation is 2028. The parameters and timing of the project will be finalised in a feasibility study.
- Rehabilitation of 220-500 kV OHTLs at KEGOC, Phase II.
- The aim of the project is to improve the reliability of Kazakhstan’s NPG through the rehabilitation of existing transmission lines that either have reached or will reach their standard service life in the coming years.
- The project covers 48 overhead lines of 220-500 kV of Akmolinskiye, Tsentralnye, Vostochnye, and Severnye MES branches with a total length of 4,236 km. The feasibility study is in progress.
- Rehabilitation of 220-500 kV OHTLs at KEGOC, Phase III.
- This project necessitates from the following reasons:
- some overhead lines of 220-500 kV have reached and exceeded their standard service life;
- reliability of electricity supply to consumers, electricity transmission, and evacuation of electricity form power plant shall be enhanced.
- The project will cover 44 overhead lines of 220-500 kV of Almatinskiye MES, Tsentralnye MES, and Yuzhnye MES branches with a total length of 4,332 km. The feasibility study is in progress.
Network
Reliability
The Republic of Kazakhstan’s core industries, such as metallurgy and oil and gas production, are marked by high energy intensity, hence the electrical industry is significant for the nation. Accordingly, a consistent and high-quality energy supply to customers is crucial to the competitiveness of Kazakhstan’s economy and the quality of life of the population.
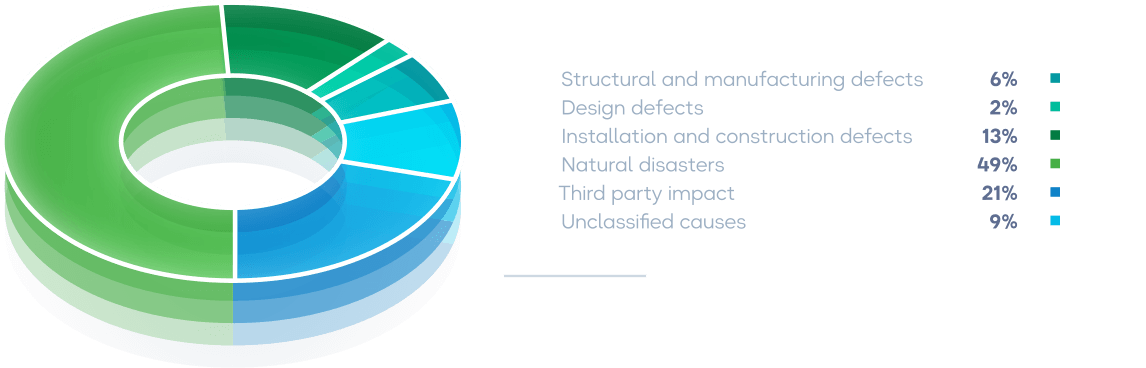
41 technological failures on lines and 12 technological failures on substations were among the 53 level II faults that the Company observed and investigated in 2022. There weren’t any serious mishaps or breakdowns. Compared to 2021, this performance measure increased by 28.4%.
Technological failure by features
International practice uses the following indices to assess the level of network reliability:
SAIDI
(System Average Interruption Duration Index) – describes the average duration per system outage per year in minutes.
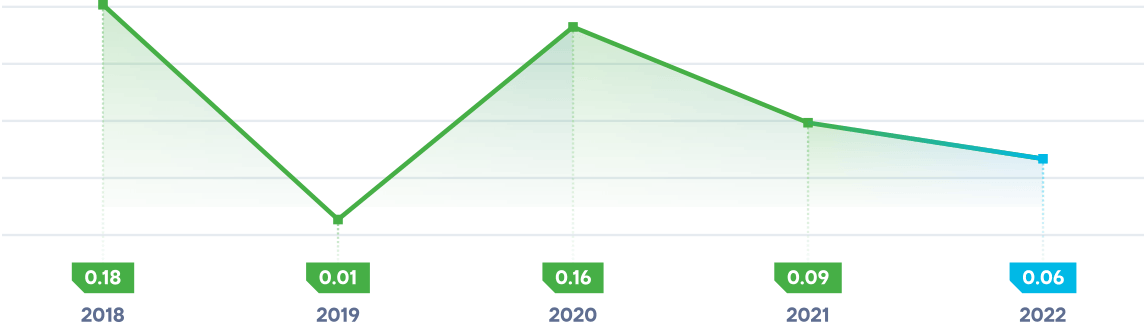
SAIFI
(System Average Interruption Frequency Index) – describes the average frequency of power outages for consumers.
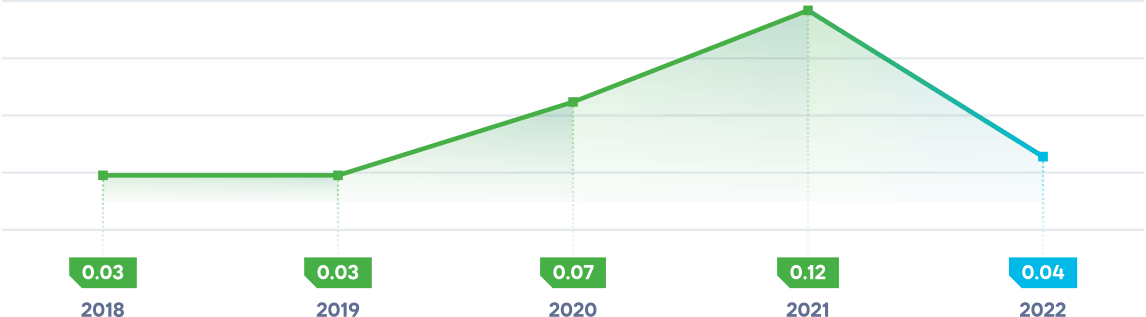
Natural occurrences were the cause of 26 technological failures (49% of the total).
The climate change increases in the amount of severe and extreme weather events that endanger our facilities, such as days of high winds and rain, hail, hurricanes, cyclones, droughts, and the risk of fire and flooding, to name a few. Extreme weather and temperature fluctuations can overload the system, lowering efficiency and potentially disrupting client service.
The main unfavourable weather factors include strong winds, thunderstorm overvoltages, and natural icing and de-icing on overhead power line conductors and lightning rods. The Company has developed a risk register that takes into account climatic factors and analyses probable scenarios that the Company may face, such as weather variability and an increase in the severity and frequency of extreme weather events. The climate change risks have been incorporated into the Company’s 2022 Risk Register, which is used to manage change.
For example, climate conditions such as the impact of natural occurrences might increase the risk of operational asset failure. To mitigate this risk, the Company takes the following steps:
- training personnel in emergency and recovery operations;
- ensuring that vehicles and special equipment are prepared for emergency and recovery work;
- stocking branches with emergency supplies;
- insuring substation equipment;
- conducting emergency drills; and
- proposing innovative solutions to reduce the impact of natural occurrences on the Company’s operational assets.
Natural disasters (floods, hurricanes, earthquakes, and diseases) are exacerbated by climate change. To mitigate this risk, the Company conducts emergency drills according to the approved topics on an annual basis; participates in ‘Koktem’, ‘Kys’, and ‘Zher’, the annual national command-staff exercises to practice measures to eliminate the consequences of natural disasters (floods, hurricanes, earthquakes); and purchases personal protective equipment.
Additionally, the Company implemented the following measures to increase network reliability and lower the primary risk of operational asset failure in 2022:
- replacement of high-voltage bushings on power equipment;
- technical certification of substation equipment and transmission lines with the help of expert organisations;
- technical examination of the condition of the substation equipment and transmission lines with the help of expert organisations;
- asset modernization and rehabilitation;
- technological study of power network faults, etc.
As part of business continuity, Emergency Response Plans (ERPs) and Emergency Response Action Plans (ERAPs) specific to the Company’s operations have been developed for the business continuity process to deal with large scale emergencies.
The ERPs define the goals, ranges, and order of activities to be taken in the event of an emergency, as well as who is in charge of making sure they are done. Regular fire and emergency drills serve as a means of the ERP testing.
The ERAPs outline the steps to be followed in the event of an emergency, including the respective timeline. The most frequent emergency at the Company’s facilities may be a fire as a result of disregard for fire safety regulations and other emergencies. The emergency response plan also outlines steps to take in the event of terrorist threats, which could lead to fatalities, major property damage, or other serious repercussions. Fire Extinguishing Plans and Communication and Notification Plans, both of which are a part of the emergency response plan, are put into practise for the quick notice of the Company’s employees in the event of an emergency and for emergency response.
To check its readiness to respond to potential emergencies, the Company takes part in annual national command-staff exercises and conducts site training and seismic exercises in areas with a high risk of earthquakes (South, East, West). The thoroughness of plans development, the coherence of civil protection formations, and the actions of forces and means during emergency recovery activities at TESs are all assessed during these exercises.
Grid Availability (GA or Grid Availability, measured in percent for the reporting year) and AIT (Average Interruption Time, measured in minutes) have been named as key performance metrics for Strategic Goal 1.
At the end of the reporting year 2022, the Company’s strategic KPIs have been met and exceeded their targets:
Indicators for Goal 1
| KPI | 2018 fact | 2019 fact | 2020 fact | 2021 fact | 2022 plan | 2022 fact |
| GA, % | indicators defined in December 2021 | 99.99874 | 99.99987 | |||
| AIT, min | 6.607 | 0.682 | ||||